Top 5 Warehouse Technologies Revolutionizing Retail & Distribution in 2025
Posted on يوليو 8, 2025Feeling like warehouse tech is evolving faster than you can adapt?
Multichannel instability, labor problems, and growing fulfillment demands are all being juggled by retailers. Meanwhile, supply chain managers face decision paralysis—drowning in options without a clear path to ROI.
Welcome to 2025, where warehouse technology is no longer a nice-to-have—it’s the competitive edge separating scalable brands from operational chaos.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction: Why Warehouse Tech Is Non-Negotiable in 2025
- 2. AI-Powered WMS: From Tracking to Thinking
In this guide, we break down the Top 5 warehouse technologies of 2025 that are reshaping retail and distribution.
We won’t just name them—we’ll show you why they matter, who they’re for, and how they actually work in the real world.
Whether you’re a retail leader looking to boost fulfillment speed or a logistics pro focused on accuracy and uptime—this is your blueprint for warehouse transformation.
AI-Powered WMS: From Tracking to Thinking
“Still using your warehouse manegement system (WMS) like a digital clipboard? In 2025, it should be doing the thinking for you.”
Today’s AI-enabled Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) go far beyond static inventory records. They learn from order flow, adapt to shifting demand, and even optimize labor assignments on the fly.
Learn how to evaluate and choose the best warehouse management software based on your region.
What it Enables
-
Automated demand forecasting and replenishment
-
Intelligent SKU slotting and bin optimization
-
Dynamic labor allocation based on workload and flow
-
Real-time integration with ERP, POS, and eCommerce systems
For Retailers
-
Improved fulfillment speed and accuracy
-
Reduction in returns and misplaced inventory
-
Smarter markdown decisions and inventory lifecycle management
-
True visibility across physical stores and online channels
For Supply Chain Managers
-
Predictive alerts for potential stockouts or overstock
-
Seamless cross-system integration for better decision-making
-
Reduction in operating costs through optimized resource planning
-
Data-driven performance reporting across facilities
This technology forms the foundation of a modern, responsive warehouse—one that can scale with complexity and adapt to change without friction.
Forecasting & Labor Optimization
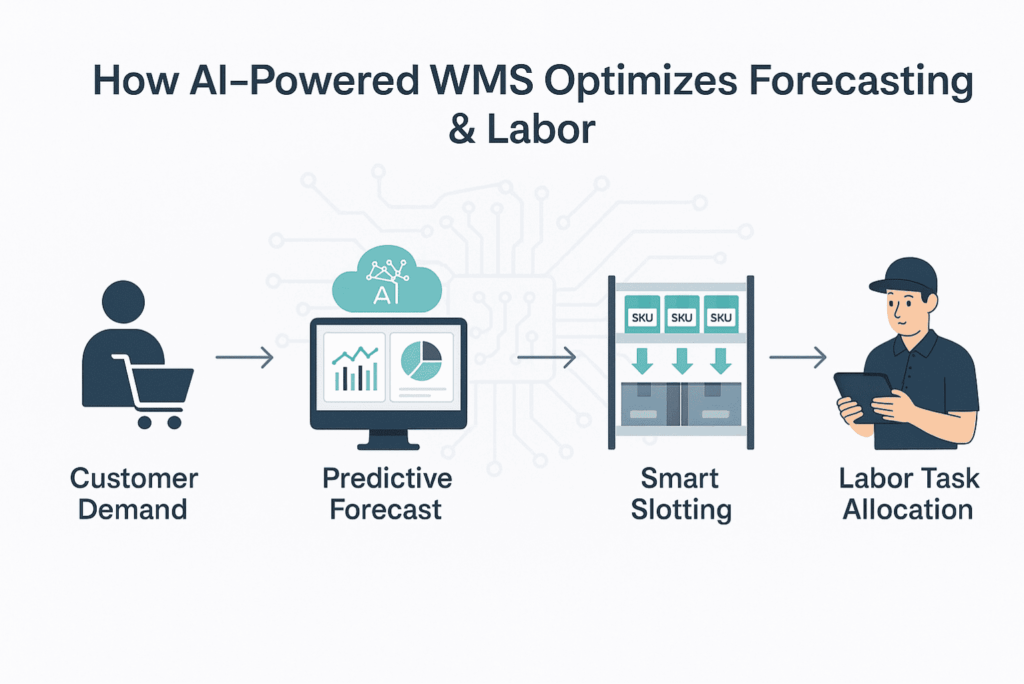
A key advantage of AI-WMS is its ability to forecast demand and dynamically allocate labor. These systems:
-
Analyze sales trends and lead times to automate reordering.
-
Identify SKU movement velocity to optimize bin locations
-
Depending on the volume of orders in real time, assign employees or robots.
-
Reduce overstaffing and idle time when demand is low.
-
Align labor plans with fulfillment SLAs (same-day, 2-day, etc.)
By combining inventory logic with workforce intelligence, AI-WMS becomes a decision-making engine—not just a tracking system.
AMRs & Robotics: Your New Warehouse Workforce
Warehouses are under pressure to accomplish more with less as labor availability tightens and fulfillment expectations rise.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and advanced warehouse robotics have emerged as critical assets—not as replacements for human workers, but as force multipliers that drive speed, precision, and operational resilience. Hardware only sticks when the core platform is right—use this decision tree to time ASRS/AMR investments.
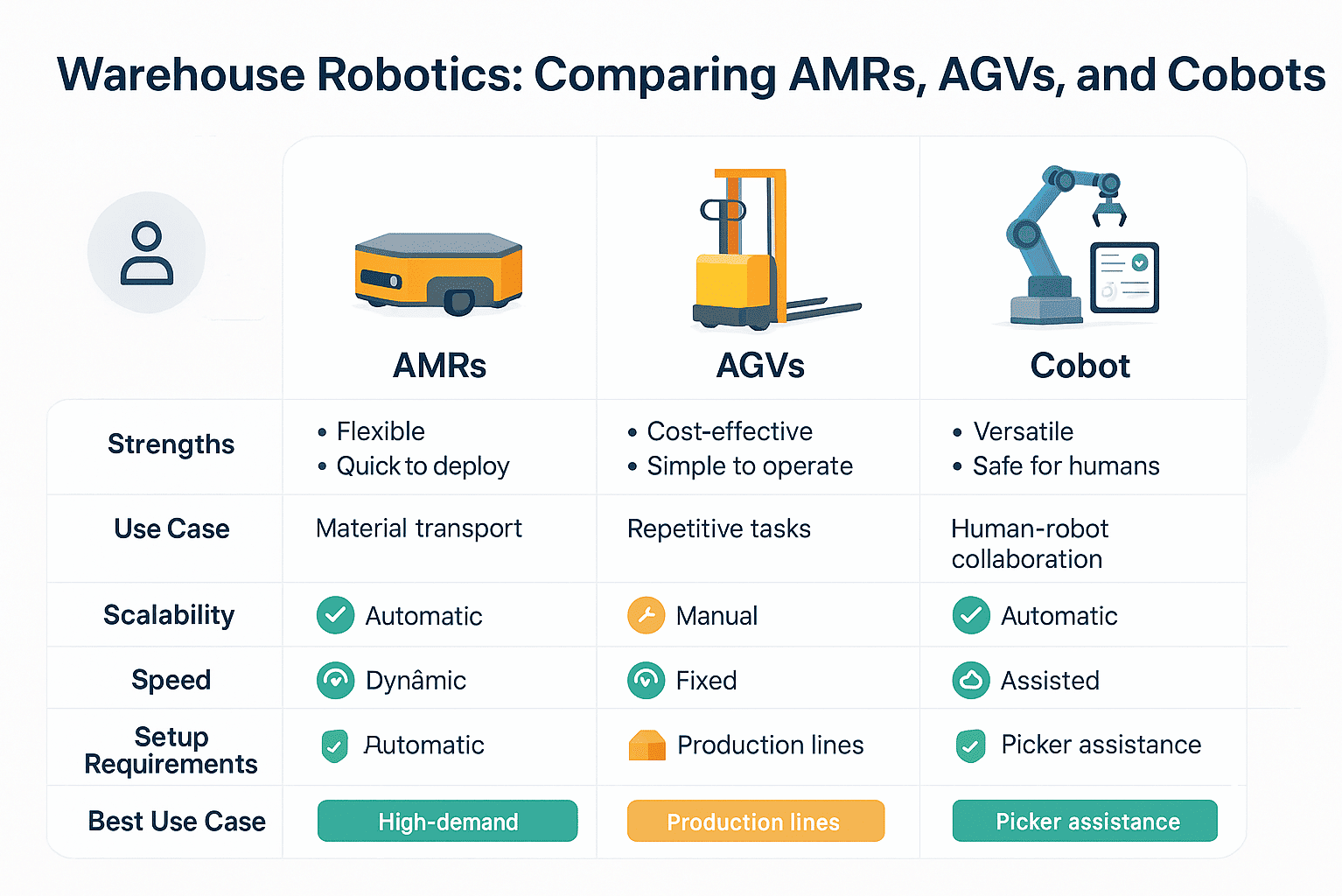
Unlike older AGV systems, which follow fixed routes, AMRs navigate dynamically using real-time data and onboard sensors. They can transport goods, retrieve items, and collaborate with human workers across variable warehouse layouts.
Discover how robotics and RFID-powered automation can work together for hands-free operations.
What it Enables
-
Scalable, 24/7 material handling across picking, packing, and sorting zones
-
Real-time navigation and route optimization based on warehouse traffic
-
Integration with WMS for task assignment, load balancing, and location accuracy
-
Flexibility to deploy quickly in existing layouts, with minimal infrastructure change
For Retailers
-
Higher throughput and quicker picking cycles at busy times
-
Lower error rates in high-SKU environments (e.g., fashion, electronics)
-
Decreased reliance on human labor for operations when hiring is scarce
-
Improved customer satisfaction through consistent fulfillment timelines
For Supply Chain Managers
-
Improved visibility into movement flows, task efficiency, and downtime
-
Ability to measure ROI by task type, robot utilization, and labor savings
-
Safer warehouse environments through automated hazard detection
-
Easier scalability across new facilities with modular robot fleets
Technology Comparison Snapshot
| Technology | Description | Best Use Cases | Scalability | Infrastructure Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMRs | Mobile, flexible, dynamic routing | Picking, transport, restocking | High | Minimal |
| AGVs | Guided, fixed-path vehicles | Heavy load transport | Medium | High (requires guides) |
| Cobots | Collaborative robotic arms | Packing, assembly, loading | Medium–High | Medium |
AMRs represent the next evolution of intelligent automation—combining precision with flexibility. For many growing warehouses, they serve as the first step toward full-scale robotic transformation
RFID & IoT: Real-Time Visibility Across Channels
Inventory inaccuracy remains one of the most costly problems in modern warehousing.
Retailers lose sales due to stockouts caused by “phantom inventory,” while distribution centers suffer from delays, shrinkage, and outdated manual counts.
In 2025, RFID and IoT-powered sensors are becoming essential infrastructure—not only for tracking inventory, but for enabling real-time visibility, environmental monitoring, and automated stock audits across the entire supply chain.
Real-time visibility is achievable with RFID inventory tracking systems designed for warehouses.
Stock Accuracy and Shrinkage Prevention
RFID tags allow warehouses to track every item or pallet without manual scanning.
When paired with IoT sensors, the system provides constant awareness of item location, condition, and movement, reducing both human error and product loss.
Key advantages:
-
Passive and active RFID systems support real-time location visibility
-
Tags can be read in bulk — no line of sight required
-
Errors during picking, replenishment, or staging are flagged instantly
-
Shrinkage (loss from theft or mishandling) is minimized through real-time alerts
-
Audits can be run without interrupting operations
Retailers benefit from accurate shelf-level visibility, while supply chain managers gain centralized oversight of stock across regions or distribution zones.
Drone Audits and IoT Monitoring
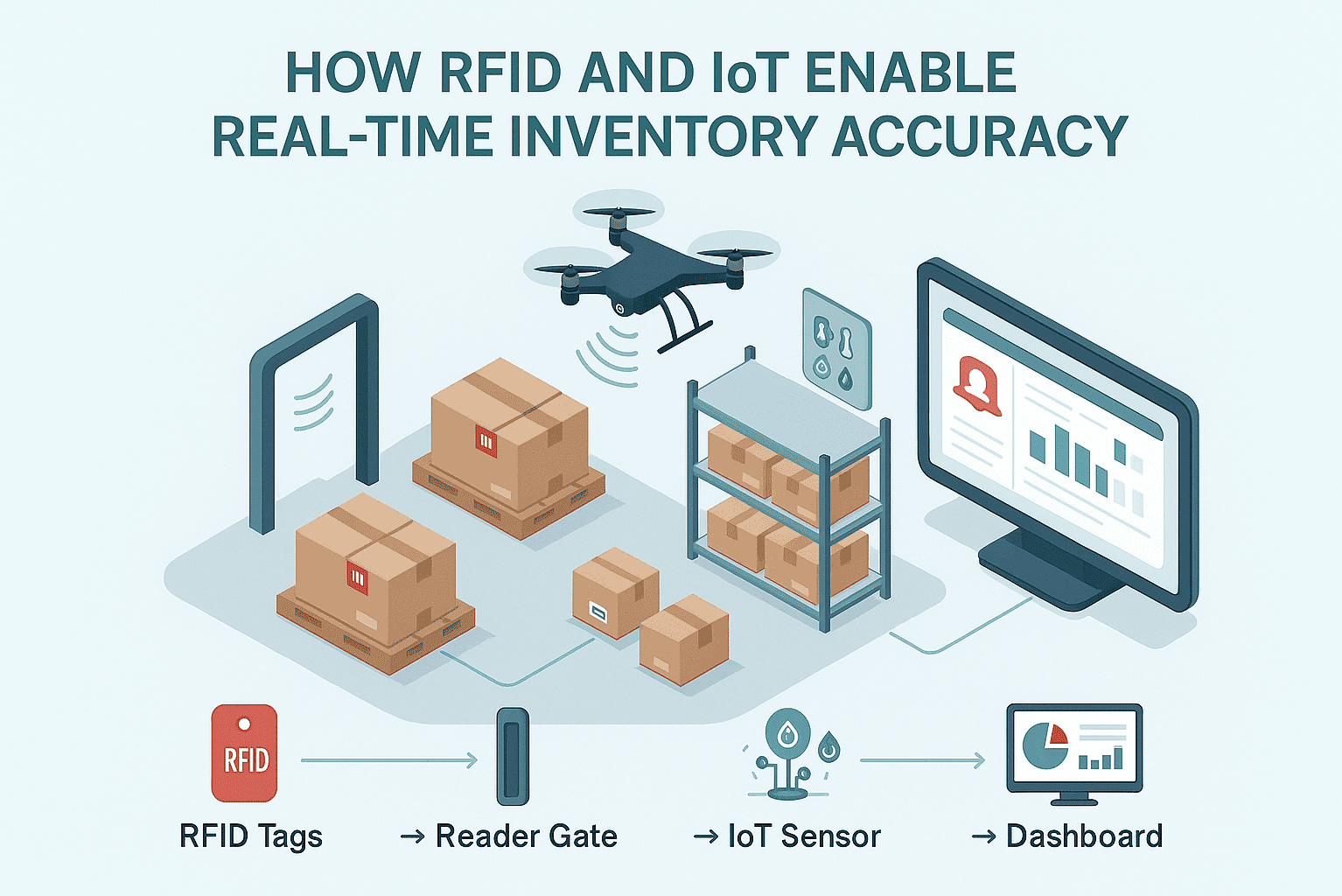
IoT devices expand visibility beyond just tracking item presence.
They monitor conditions — temperature, humidity, movement — and send alerts when risks to product quality or safety arise.
Use cases include:
-
Drones equipped with RFID readers conducting automated inventory scans
-
Real-time out-of-stock conditions are detected by IoT shelf sensors.
-
Resupply predictions based on use and movement patterns
-
Environmental controls for cold chain, pharma, or high-value goods
Combined, these tools provide the accuracy and agility required for modern fulfillment operations—without relying on manual labor.
What it Enables
-
Real-time tracking of a single product or pallet’s position
-
Real-time environmental monitoring (temperature, humidity, vibration)
-
Automated alerts for stock discrepancies or unauthorized movement
-
End-to-end inventory transparency across physical and digital channels
For Retailers
-
Precise stock visibility at the shelf, bin, or store level
-
Reduced stockouts and overselling in omnichannel environments
-
Improved customer satisfaction through accurate availability promises
-
Lower shrinkage from theft or misplaced items
For Supply Chain Managers
-
Drone-assisted inventory audits with RFID scan capability
-
Predictive analytics on stock movement, usage rates, and bottlenecks
-
Integration with ERP or WMS platforms for proactive inventory control
-
Higher data accuracy across distribution centers and in-transit shipments
Technology Spotlight: RFID vs Barcode
| Feature | RFID | Barcode |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Method | Wireless, no line-of-sight | Optical requires direct scan |
| Speed | 200+ tags/sec | 1 scan at a time |
| Range | Up to 10 meters | A few inches |
| Use Case | High-speed, high-volume environments | Static item tracking |
| Cost | Higher upfront, lower long-term labor | Low up front, manual labor cost |
RFID and IoT are visibility enablers, not just upgrades. In a warehouse network that must move quickly and scale confidently, real-time awareness is a non-negotiable foundation.
Smart Storage & Fulfillment: Speed Meets Density
In today’s fast-moving retail and distribution landscape, square footage is no longer a passive cost—it’s a strategic asset.
Warehouses that cannot efficiently store, access, and fulfill inventory are forced into costly expansion, underutilized space, or fulfillment delays.
Smart storage systems—such as AS/RS (Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems), cube-based storage, and micro-fulfillment centers—offer a high-density, high-efficiency solution. When integrated with advanced picking technologies, they enable faster order processing with fewer errors and less labor.
ASRS, Cube Storage, Micro-Fulfillment
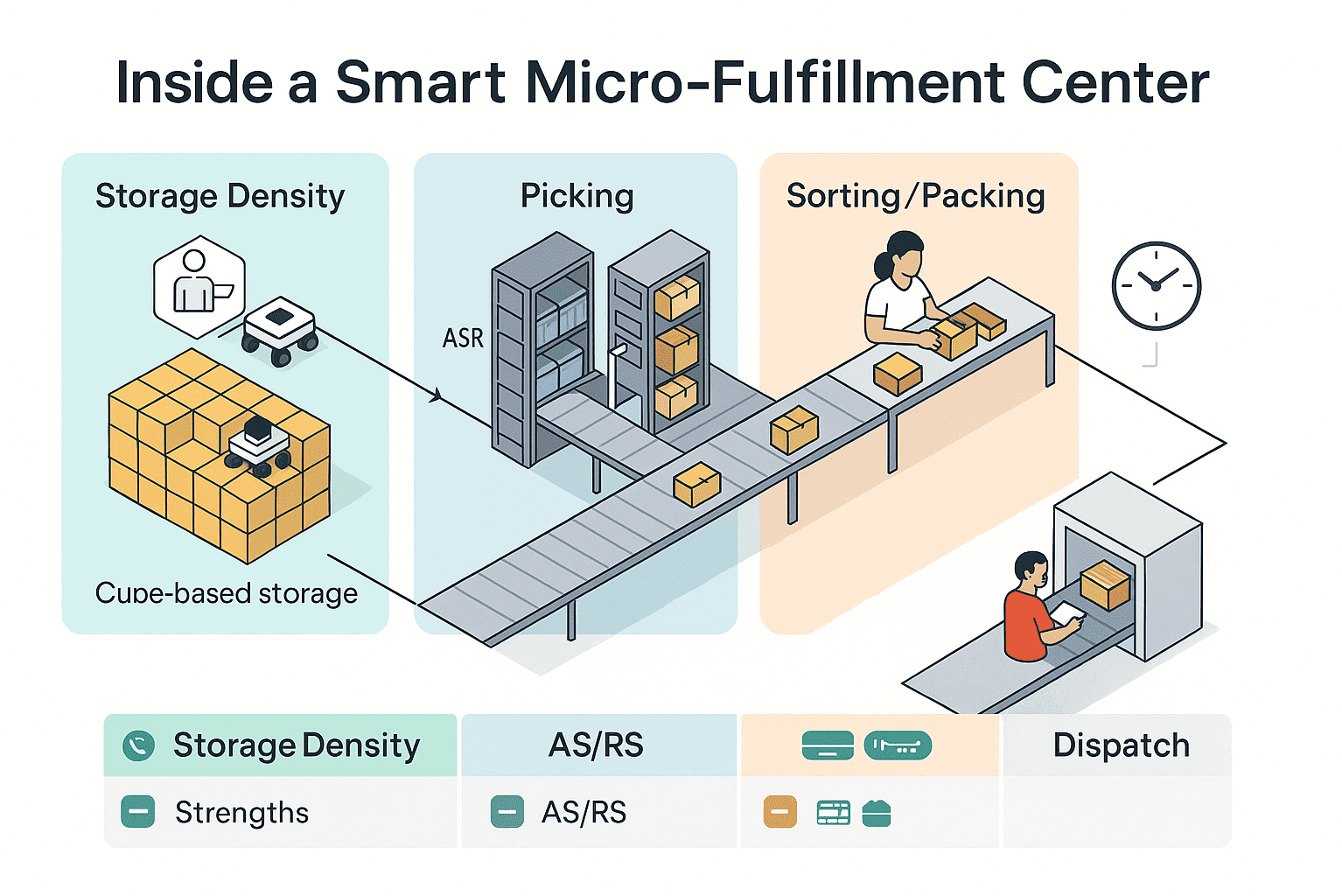
These systems are designed to store more SKUs per square foot and retrieve items with minimal human effort.
Core technologies include:
-
AS/RS (Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems): Computer-controlled shelving that delivers products to workers or robotic arms
-
Cube Storage Systems: 3D storage models (e.g., AutoStore) that reduce aisle space and increase volume density
-
Micro-Fulfillment Centers: Compact, modular facilities located close to urban hubs to handle rapid eCommerce fulfillment
Benefits:
-
Much quicker order processing, particularly in settings with a high SKU or turnover
-
Lower picking labor per order
-
Smarter storage logic integrated with WMS for dynamic inventory slotting
-
Reduced warehouse footprint without compromising throughput
Micro-fulfillment reduces last-mile delays and helps prevent costly stockouts.
Matching Layouts to Product Types
Not all inventory functions the same, and no two warehouses need the same layout.
Mapping storage types to inventory profiles is a key component of contemporary fulfillment strategies:
| Product Profile | Recommended System | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| High-volume, fast-moving | Conveyor-fed AS/RS | Speed + automation |
| Multi-SKU, compact items | Cube storage | Density + flexibility |
| Last-mile eCommerce | Micro-fulfillment | Proximity + rapid response |
| Seasonal or bulky items | Traditional racking + robotic picking | Scalability + cost control |
Smart storage planning isn’t just about space — it’s about aligning product flow, labor availability, and delivery timelines with infrastructure that adapts.
What it Enables
-
Automated vertical or compact product storage and retrieval
-
Intelligent put-away and picking sequences based on SKU velocity
-
Conveyor, AMR, and WMS integration for smooth fulfillment
-
Real-time inventory availability in high-volume, multi-SKU environments
For Retailers
-
Quicker pick-and-pack times for retail and eCommerce orders
-
Higher order accuracy and fewer returns
-
Lower space costs per unit stored
-
Capability to meet next-day or same-day shipping commitments
For Supply Chain Managers
-
Optimized inventory slotting with reduced travel paths
-
Increased cubic storage utilization (especially in urban or last-mile facilities)
-
Compatibility with robotic systems for end-to-end automation
-
Improved forecasting from clearer demand and movement data
Decision Intelligence: Choosing the Right Tech Stack
With dozens of emerging technologies on the market, the real challenge isn’t knowing what’s available — it’s knowing what’s worth investing in.
2025 will be the year businesses either upgrade with purpose or get overwhelmed by scattered implementations.
That’s why leading retailers and supply chain teams are adopting decision frameworks to guide investments based on ROI, scalability, and alignment with current infrastructure.
What to Consider When Selecting Warehouse Technologies
-
Compatibility with current ERP, OMS, or WMS systems
-
Integration Time and Complexity—APIs, middleware, and support
-
Total Operations Cost (TOC)—not just purchase price, but labor impact, downtime reduction, and long-term ROI
-
Scalability and Modularity: Can the system expand to accommodate your business?
-
Vendor Track Record—support, deployment success, use-case validation
Many of these tools only deliver value when they address inventory challenges as warehouses scale, rather than being deployed as isolated technologies without process alignment.
Technology Comparison Matrix
Among the most practical upgrades, cycle counting automation tools drive immediate efficiency wins.
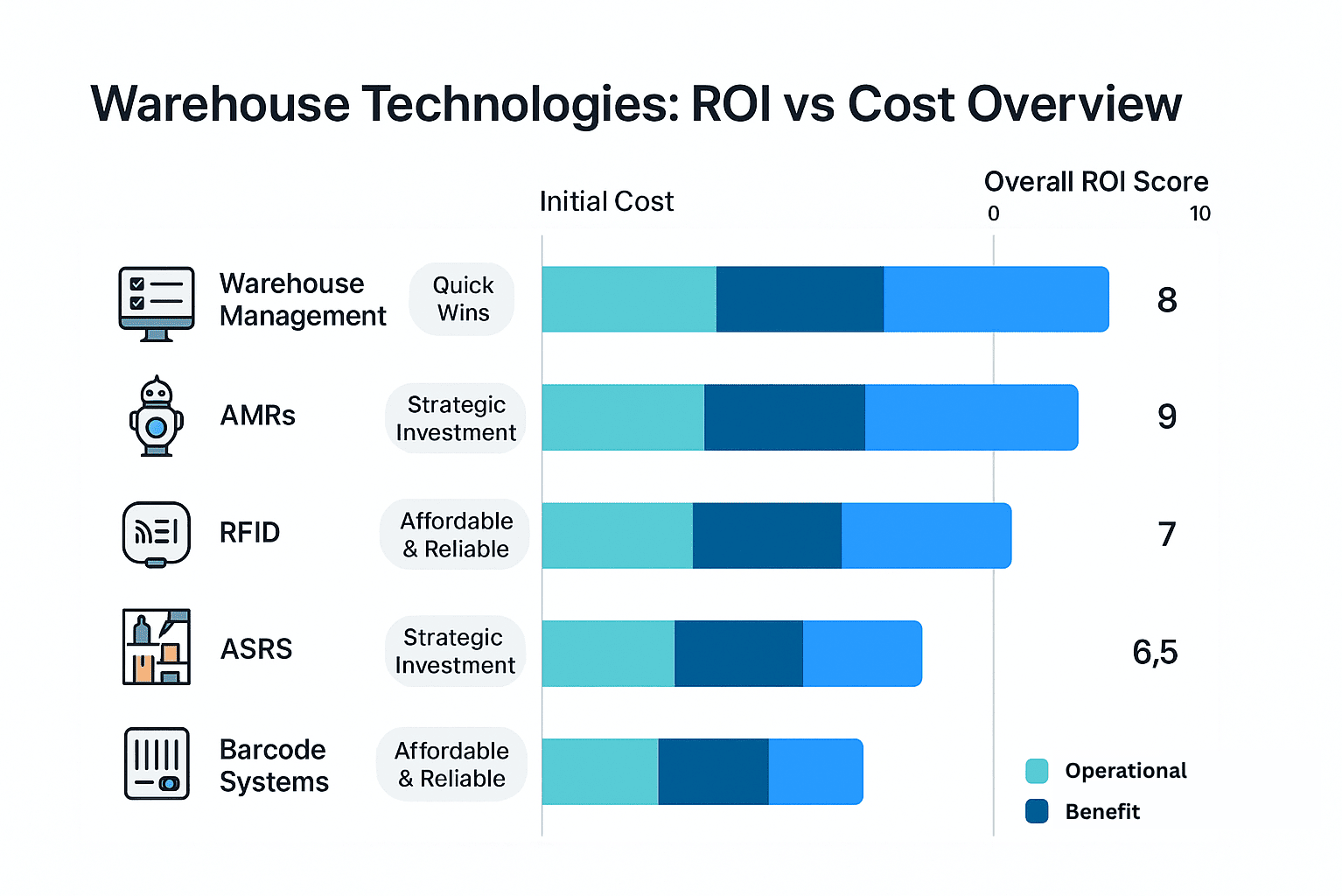
| Tech | Best Use Case | Maturity | Initial Cost | Long-Term ROI | Ease of Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFID | Real-time stock tracking, loss prevention | High | Moderate | High | High |
| Barcode Systems | Low-cost inventory tracking | Very High | Low | Medium | Very High |
| AI-WMS | Forecasting, labor optimization | Emerging–Strong | High | Very High | Moderate |
| AMRs | Goods movement, order picking | High | High | High | Medium |
| AS/RS | Dense storage and retrieval | High | High | High | Medium |
ROI Evaluation Strategy
Before implementing new warehouse technologies, organizations should apply a strategic evaluation framework:
See how smart forecasting tools like Slimstock optimize stock levels and ROI.
1. Start with TOC (Total Operations Cost)
-
Include direct costs (equipment, software, integration)
-
Estimate savings from labor reduction, error reduction, and faster fulfillment
-
Project ROI over 12–36 months based on use case
2. Use Pilot Testing
-
Validate effectiveness in a controlled environment
-
Gather performance metrics (cycle time, accuracy, user adoption)
-
Evaluate downtime risk, employee adaptation curve, and vendor support quality
3. Align Tech to Scalability Goals
-
Will this technology grow with your volume?
-
Can it be deployed across multiple sites or environments?
-
Is the vendor committed to innovation and long-term support?
Choosing a warehouse tech stack is no longer about selecting software — it’s about building a future-ready operational foundation.
For Retailers
-
Focus on solutions that directly impact fulfillment speed and customer satisfaction
-
Prioritize plug-and-play systems with fast ROI: RFID, AI-WMS, AMRs
-
Consider vendor ecosystem and training support to minimize disruption
For Supply Chain Managers
-
Look for modular systems that can be deployed across multiple sites
-
Evaluate total lifecycle cost over 3–5 years, including maintenance and retraining
-
Use pilot programs and limited deployments to validate tech fit before full rollout
This is not the time to chase trends. It’s time to select technologies with intention—based on your operational priorities, growth plans, and the readiness of your existing stack. The next wave of innovation isn’t just about automation — it’s about integration. Explore why businesses are upgrading to smarter inventory platforms to stay ahead of warehouse modernization trends in 2025 and beyond.
Ready to Future-Proof Your Warehouse?
2025 isn’t the future — it’s already here.
Smart warehousing is no longer reserved for global giants. With the right technologies, even mid-sized retailers and distribution networks can compete on speed, accuracy, and operational intelligence.
Not sure which tools are right for your environment?
We’ll help you evaluate your current setup, define your growth goals, and recommend a tech stack built for real ROI — not just buzzwords.
→ [Book a Strategy Call]
Get personalized insights tailored to your warehouse model and business priorities.