RFID vs. Barcode Inventory Tracking (2025): Cost, Speed & Accuracy Breakdown for Logistics Managers
Posted on يوليو 15, 2025Table of Contents
-
- RFID vs Barcode: Why This Decision Still Matters in 2025
- Feature Comparison Table: RFID vs Barcode vs QR
- Why Barcode Systems Break Down (And When RFID Doesn’t Help Either)
- Barcode Fatigue & Scan Accuracy: Hidden Costs of Manual Tracking
- RFID in the Real World: The Operational Challenges No One Tells You
- Metal, Liquids & Interference: The RFID Enemies in Your Warehouse
- Hybrid Inventory Tracking Strategy: When to Use RFID, Barcode, or Both
- WMS, ERP & Automation: How Each System Integrates (or Collides)
- Cost, Speed & Accuracy Breakdown Matrix for 2025
- Decision Framework: Which System Is Right for Your Warehouse?
RFID vs Barcode: Why This Decision Still Matters in 2025
RFID isn’t new. Barcodes aren’t dead. But in 2025, the way you choose between them will either streamline your entire supply chain or quietly drain thousands from your bottom line. Logistics managers today aren’t asking what these systems are. They’re asking, Which one gives me the edge I need to scale faster, fulfill cleaner, and reduce the chaos?
Why Barcode Still Dominates Warehouses (Even in 2025)
-
Over 70% of global warehouses still rely on barcode scanning
-
Reasons: simplicity, low-cost entry, compatibility with existing WMS
-
But: manual scanning → human fatigue, scan delays, and data errors
“Barcode systems persist not because they’re perfect—but because they’re just good enough to not be questioned.”
The Modern Logistics Manager’s Dilemma
-
High-volume ops need speed + accuracy—barcodes slow at scale
-
RFID adoption is growing but brings cost and complexity
-
Pressure to digitize is rising (AI, automation, real-time fulfillment)
“You’re not just picking between tech — you’re designing the backbone of how your warehouse moves.”
RFID Adoption Is Real—But Full Utilization Is Rare
-
Big players (Zara, Amazon, Decathlon) have rolled out RFID
-
But mid-sized operations often:
-
Start rollout → abandon due to signal interference or unread tags
-
Struggle with ROI justification
-
-
Surface-level adoption ≠ operational success
“RFID seems sophisticated… until your reader misfires and your WMS records the wrong count.”
So before we get lost in marketing promises, let’s look at the hard numbers. Here’s how RFID, Barcode, and QR stack up when it comes to raw features. For ongoing accuracy, software-driven cycle counting complements either RFID or barcode strategies.
Feature Comparison Table: RFID vs Barcode vs QR
Before you commit to a new tracking system, let’s look at how RFID, Barcode, and QR code technologies truly compare—across the metrics that actually impact warehouse operations: cost, speed, accuracy, durability, and integration.
| Feature/Factor | RFID | Barcode | QR Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Type | Radio frequency (no line of sight needed) | Optical (requires line of sight) | Optical (requires line of sight) |
| Read Speed | Bulk scan: 100+ items/second | One-by-one manual scanning | Moderate (slightly faster than barcode) |
| Accuracy | High (if properly configured) | High (operator-dependent) | Moderate to high |
| Durability | Withstands heat, chemicals, rough handling | Susceptible to scratches/fading | Prone to damage, especially in harsh environments |
| Range | Up to 10–30 ft (UHF) | 6–24 inches | 3–6 inches |
| Data Capacity | High — can store 100s of bytes or more | Very limited | Moderate — 4,000+ alphanumeric chars |
| Infrastructure Cost | High (readers, tags, middleware) | Low | Very low |
| Implementation Time | Medium to high | Fast & simple | Fast |
| WMS/ERP Integration | Requires middleware; advanced sync | Natively supported in most WMSs | Depends on system |
| Best Use Case | Large warehouses, high-value SKUs, automation | Most warehouses, low to mid SKUs | Asset tracking, labeling, mobile ops |
Speed Isn’t Everything—It’s About the Right Speed
RFID is built for bulk visibility—but that doesn’t always equal precision. If your operation deals with mixed pallets, fragile packaging, or metal racks, speed without context = chaos.
Barcodes are slower, yes. But in low-SKU, high-accuracy workflows, they still outperform RFID. Learn how these technologies integrate in top UAE warehouse software.
When Cheap Gets Expensive
QR and barcode systems look great on paper—until your team scans 600 labels a day and fatigue kicks in. Or a torn label forces manual entry.
RFID has a higher startup cost, but over time? It removes bottlenecks and reduces touchpoints—especially at inbound, cycle counts, and bulk audits.
Of course, features don’t always translate to performance. Many logistics managers choose based on tech specs—then face failure during real-world deployment.
Let’s talk about that next.
Why Barcode Systems Break Down (And When RFID Doesn’t Help Either)
Warehouse ops don’t fail on paper—they fail on the floor. And no feature chart can prepare you for that moment when your cycle count is off by 8%, or your picker wastes 3 hours re-scanning items due to a misprint. Barcode scan errors and missed reads are major contributors to inventory discrepancies and hidden costs that most teams overlook.

Here’s where barcode tracking actually breaks—and why RFID doesn’t always save you either.
End-of-Year Chaos: When Barcode Systems Get Crushed
-
1-by-1 scanning = exhausting during full-cycle counts
-
High error rate due to operator fatigue
-
Label quality issues (smudges, misalignment, worn out)
In Q4 alone, some warehouses report 20–30% longer cycle count times using barcode-only systems
Ghost Inventory & Phantom SKUs
-
Damaged barcodes → not scannable → skipped items
-
Shrinkage goes unnoticed
-
Manual entry = human error = SKU mismatches
Even one missed scan can create downstream chaos—especially in multi-DC operations.
When RFID Doesn’t Help Either
-
Improper tag placement = missed reads
-
Readers scanning through metal shelves = duplicate reads
-
No signal calibration = unintentional scanning of neighboring areas
RFID sounds frictionless—until your reader misfires and inflates your pick count by 15.
“We switched to RFID expecting magic. What we got was 3 months of tuning, missed reads on metal bins, and retraining the floor team twice.”
— Senior Ops Lead, Mid-size 3PL
Whether it’s a scanner slowing down a picker or an RFID tag refusing to read under pressure—both systems carry hidden costs.
Next, let’s unpack one of the least talked-about—but most costly—factors: human fatigue.
Barcode Fatigue & Scan Accuracy: Hidden Costs of Manual Tracking
Inventory tracking doesn’t live on spreadsheets—it lives in the hands of tired warehouse operators, scanning hundreds of SKUs per shift.
And when fatigue sets in, your inventory data pays the price. Let’s talk about the costs nobody factors into the budget.
The Hidden Burnout Behind Barcode Scanning
-
Manual scanning = repetitive stress on pickers, receivers, cycle counters
-
Productivity drops as shift progresses
-
High-scan environments (300–600 scans/day) lead to:
-
Missed scans
-
Wrong scans
-
Skipped items
-
“It’s not about whether barcode works — it’s whether your team can keep up with it.”
Accuracy Is High… Until It Isn’t
-
Barcodes are 99% accurate when scanned properly
-
However, when you combine tiredness with haste, the result is either mis-scanning of SKUs, omission of tags, or duplication of scans for identical items.
-
Inventory mismatch leads to:
-
Wrong picks
-
Order delays
-
WMS conflicts
-
“In warehouses where cycle counts run late into the night, barcode accuracy can drop by 5–10%.”
The Real Cost of Error-Correction Loops
-
Bad scans mean rework, recounts, or manual overrides
-
Time lost in fixing → orders delayed
-
Staff trust in the system erodes over time
Every time a picker stops to fix a scan error, you lose momentum—and in high-throughput ops, that kills fulfillment velocity.
- Scanner fatigue = overtime
- Errors = customer service headaches
- Fat-finger entries = systemic inventory rot
So if barcode scanning comes with human limits, is RFID the fix-all solution?
Not quite. RFID brings its own set of operational challenges most warehouses don’t anticipate—and often don’t budget for.
RFID in the Real World: The Operational Challenges No One Tells You
RFID gets sold as seamless. Fast scans, no line of sight, minimal labor. But logistics managers know the truth: RFID is only as good as your environment, your integration, and your team’s ability to adapt.
Let’s break down what really happens after the tags are ordered.
The Setup Isn’t Instant — It’s Iterative
-
Reader placement, antenna calibration, tag positioning all require site testing
-
UHF tags behave differently depending on
-
Floor layout
-
Ceiling height
-
Metal proximity
-
Temperature and moisture levels
-
“It’s not plug-and-play—it’s test, calibrate, and test again.”
Tag Calibration Can Wreck Early Confidence
-
Tags on metal bins? You need isolation pads
-
Tags on pallets wrapped in plastic? Expect signal bounce
-
Tags on mixed-SKU loads? You’ll scan what you didn’t mean to
“The system that scanned 30 items flawlessly in the lab? It’ll read 67 tags in the warehouse—including 12 from the next aisle.”
Your Team Isn’t Ready (Unless You Train Them)
-
RFID workflows feel alien at first: no beeps, no aiming, no trigger pulls
-
Teams often
-
Walk too fast → missed scans
-
Don’t trust the system → re-check manually
-
Place tags incorrectly → data errors
-
“Without training, RFID systems become expensive ghosts—technically on, but practically ignored.”
- Wrong tag orientation
- Dirty readers
- Reader scanning through walls
- Staff confusion
- Poor WMS sync
And even if your rollout goes well… You’re not done yet. RFID has a secret weakness that most systems can’t overcome: its vulnerability to the warehouse itself.
Let’s talk about metal, liquids, and interference zones.
Metal, Liquids & Interference: The RFID Enemies in Your Warehouse
No RFID system is immune to its surroundings. If your warehouse contains metal racks, liquid packaging, forklifts, dense pallets, or reflective surfaces, your tags might scan twice—or not at all.
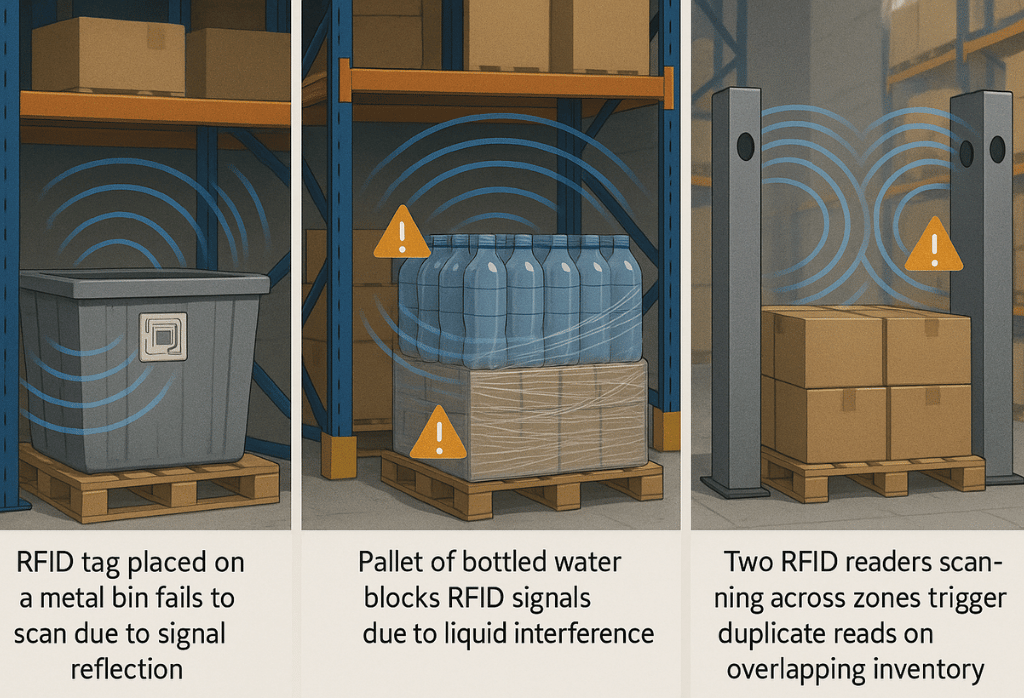
Welcome to the invisible battlefield of RFID performance.
Metal Kills Signals (Unless You Adapt)
-
Metal reflects radio waves → signal bounce → false reads or missed tags
-
Common issues:
-
Tags inside metal bins = dead zones
-
Readers near steel racking = phantom tag reads
-
-
Solution:
-
Use metal-mount tags with shielding foam
-
Space out reader zones to avoid echo pickup
-
“Tagging a steel part with a regular RFID label is like shouting into a mirror—all you get is noise.”
Liquids Absorb Frequencies
-
Water and liquid-heavy goods (beverages, chemicals) = RFID signal blockers
-
Wrapped pallets of bottled water often go dark to RFID readers
-
Risk: Stockouts or false out-of-stock alerts
“Think of liquid like a sponge — it soaks up the signal before the tag can respond.”
Interference Zones That Sabotage Clean Reads
-
Reader overlap = duplicate scans
-
Adjacent dock doors = scanning each other’s pallets
-
Forklifts with RFID readers? May trigger unwanted read events. For a deeper look into how RFID works at the operational level, check out our full breakdown of RFID warehouse tracking systems.
“In one case, a forklift reader scanned boxes sitting 3 bays away — adding phantom units to the order.”
- Dock doors (especially near loading/unloading bays)
- Dense rack clusters with metal scaffolding
- Areas with mobile readers on forklifts
- Inbound lanes with mixed-SKU pallets
These environmental constraints are why no single system wins outright.
Many operations find the real power lies in blending technologies — each used where it performs best.
Let’s explore that next.
Hybrid Inventory Tracking Strategy: When to Use RFID, Barcode, or Both
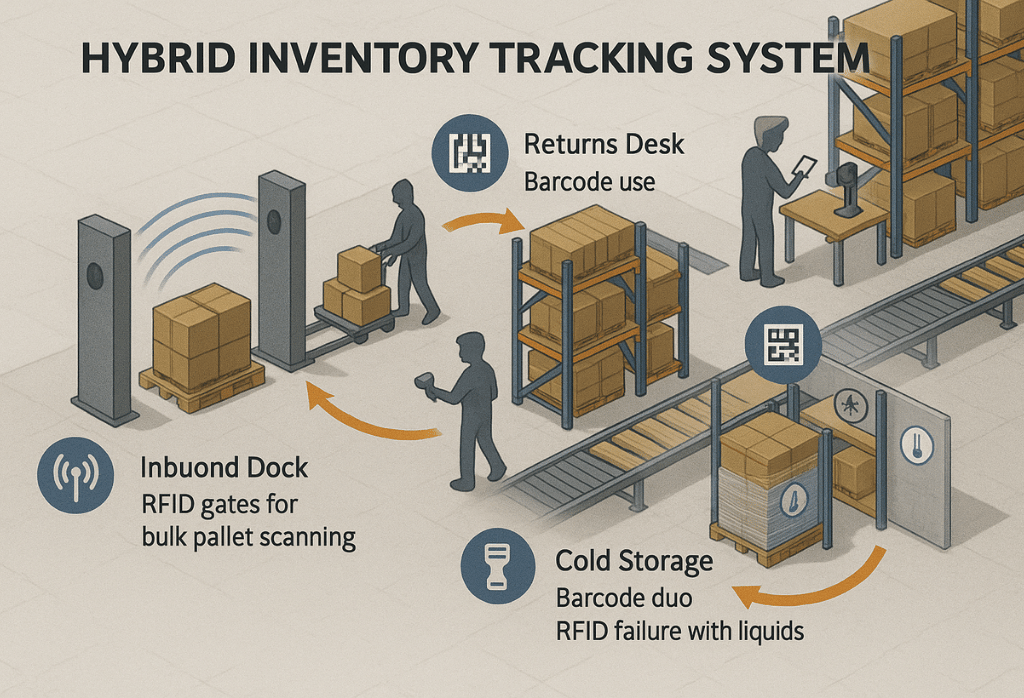
RFID isn’t here to kill barcode — and QR codes aren’t just for marketing gimmicks. RFID-enabled zone scans can also be integrated into non-disruptive cycle counts to boost speed without halting operations.
The most resilient, scalable, and accurate warehouse tracking strategies in 2025?
They use all three — in the right places, at the right time.
Barcode Where You Need Simplicity & Precision
-
Perfect for:
-
Low to mid-SKU environments
-
Manual pick/pack/ship workflows
-
Receiving and labeling goods
-
-
Integrates natively with most WMS
-
In areas with a high metal content and a large amount of liquid, where RFID does not work, it is extremely dependable.
-
Requires little to no retraining
“When accuracy is non-negotiable and budgets are lean, barcode remains king.”
RFID Where You Need Speed & Volume
-
Ideal for:
-
Bulk receiving and pallet movement
-
High-throughput cross-docking
-
Cycle counts in large facilities
-
-
Works without line-of-sight
-
Reduces operator fatigue during repetitive scanning
“”RFID is about releasing workers from the grunt work, not about replacing them.”
QR Codes Where Flexibility Is Critical
-
Best suited for:
-
Returns processing
-
Temporary inventory
-
Mobile scanning with smartphones
-
-
Cost-effective and printable anywhere
-
Easy to generate dynamically for assets or locations
“QR fills the gap when you need lightweight, mobile-first inventory tagging.”
| Zone | Recommended Tech | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Inbound Dock | RFID | Bulk pallet identification, no line-of-sight needed |
| Picking Zone | Barcode | Human-led picking, high scan precision |
| Returns Desk | QR Code | Fast reprocessing, smartphone scanning |
| Cold Storage | Barcode | RFID fails in liquid-heavy zones |
| Outbound Verification | RFID + Barcode | Speed + double-check accuracy |
“This isn’t tech overkill. It’s tech alignment. Each tool plays its role in reducing errors, stress, and operational cost.”
Of course, your tech strategy is only as strong as your system integration.
So next, let’s look at how RFID, barcode, and QR interact with your WMS, ERP, and warehouse automation stack.
WMS, ERP & Automation: How Each System Integrates (or Collides)
A tracking system isn’t just about what’s on the label — it’s about what happens after the scan.
If your RFID tag scans perfectly but your WMS doesn’t know what to do with it, you’ve got a visibility black hole. Want a broader view of why enterprises are investing in RFID? Explore the core benefits of RFID inventory management in our strategy guide.
Let’s talk integration friction — and where each tech shines behind the scenes.
Native Sync, Proven Stability with Barcode + WMS
-
Most WMS platforms (NetSuite, SAP, Zoho, Fishbowl) are built around barcode scanning
-
Barcode scanners act as plug-and-play USB input or mobile apps
-
Easy to configure with:
-
SKU-level rules
-
Location transfers
-
Lot/batch tracking
-
-
Minimal infrastructure investment
“Barcodes are the native language of inventory software. No translation needed.”
RFID Needs Middleware (But Pays Off When Done Right)
-
RFID data is continuous — not one-scan-one-action
-
Needs middleware (e.g., Zebra, Impinj, SML platforms) to:
-
Filter reads
-
De-duplicate scans
-
Sync events to WMS or ERP
-
-
Good systems = seamless visibility
-
Bad setups = data noise, phantom SKUs
“RFID is an event stream, not a substitute for barcodes. Additionally, you must train your WMS to listen.”
QR Codes Work Best with Lightweight, Cloud-Based Systems
-
Most WMS platforms don’t natively support QR-specific workflows
-
BUT: QR works great in:
-
Mobile inventory apps
-
Field logistics systems
-
Low-tech environments using Google Sheets + Zapier-style automation
-
-
Dynamic QR code generation = high flexibility
“QR codes integrate where barcode would require hardware — and RFID would be overkill.”
Common Integration Pitfalls (and How to Avoid Them)
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Tag scans not showing in WMS | Reader not mapped to inventory location | Middleware event routing |
| Duplicate entries | Reader range not calibrated | RFID antenna tuning |
| Barcode mismatch errors | Label print config vs WMS SKU naming | Labeling standardization |
| QR code unreadable in app | Poor resolution or lighting | Use high-contrast QR with mobile-friendly readers |
Choosing your tracking system isn’t just about hardware — it’s about how cleanly your data flows from the dock floor to your dashboard.
Now let’s get brutally clear on the numbers: How does each system perform in real-world ROI?
Cost, Speed & Accuracy Breakdown Matrix for 2025
Features are great. Integration matters. But in the end, your tracking system has to prove its worth in speed, accuracy, and ROI — or it becomes an expensive bottleneck. If you’re scaling across multiple sales channels, you’ll want to explore how smart warehousing supports omnichannel retail through hybrid tracking systems
Let’s break down how RFID, Barcode, and QR actually perform in the warehouse trenches.
Master Matrix Table
| Factor | RFID | Barcode | QR Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. Read Speed | 100+ tags/sec (bulk) | 1 tag/sec (manual) | ~2–3 tags/sec (manual) |
| Accuracy | 98%+ with tuning | 96–99% (dependent on operator) | 90–95% (scan quality matters) |
| Operator Effort | Low (hands-free) | High (manual scanning) | Medium |
| Fatigue Risk | Low | High | Medium |
| Implementation Time | 2–6 months | 2–3 weeks | <1 week |
| Infrastructure Cost | $$$ (Tags + Readers + Middleware) | $ (Scanners + Labels) | $ (Smartphones + Printers) |
| Tag/Label Cost | $0.15–$2.00 per tag | $0.01–$0.05 per label | $0.02–$0.10 per label |
| Integration Complexity | High (requires middleware) | Low (WMS native support) | Medium (cloud/mobile systems) |
| Best Fit | Large-scale, automated ops | Mid-sized, human-led ops | Flexible/lightweight ops, returns, field logistics |
Speed Gains Are Real — But Only If You Can Use Them
-
RFID shines on bulk pallet receiving, cycle counts, zone scanning
-
Barcode is still faster per item when human control is needed
-
QR is limited by camera performance, but wins in mobile workflows
“The fastest system is the one that fits your process — not just your wishlist.” See when automation actually pays back in a multi-warehouse stock control rollout (with ROI formulas).
Accuracy Is More Than a Percentage
-
Barcode misreads often traced to:
-
Fatigue
-
Label damage
-
Rush errors
-
-
RFID requires tuning to avoid false reads
-
QR accuracy depends on scan quality + lighting
“It’s not about 1% difference — it’s about whether your 1% triggers a $5,000 recount.”
What ROI Actually Looks Like
| Scenario | RFID | Barcode | QR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large DC with 100K SKUs | High ROI (if deployed right) | Slower throughput, high labor cost | Limited use |
| 10K SKU warehouse, 15 staff | ROI takes longer | Strong ROI, fast setup | Great for returns/mobile ops |
| eCom brand with distributed inventory | Moderate ROI | Works well | Great as mobile extension or in 3PL sync |
“If you’re not doing 100+ reads per zone per hour — you probably don’t need RFID everywhere.”
At this point, you’ve seen the truth behind cost, accuracy, and performance.
Now let’s put it all together. Use this decision framework to choose what actually works for your warehouse — not just what’s trending.
Decision Framework: Which System Is Right for Your Warehouse?
By now, you know the truth: there’s no perfect tracking system — only the one that matches your warehouse’s needs, budget, and operations flow.
Use this framework to filter out the noise and lock in your decision.
Start Here — How Complex Is Your Operation?
| Question | If YES → | If NO → |
|---|---|---|
| Do you manage 50K+ SKUs across zones? | RFID | Barcode |
| Are most of your picks still manual? | Barcode | RFID or Hybrid |
| Do you use forklifts or mobile carts? | RFID (with zone readers) | Barcode / QR |
| Do you need mobile-first field tracking? | QR | RFID/Barcode |
| Do you operate in metal/liquid-heavy environments? | Barcode | RFID (only with tuning) |
Budget Fit vs Performance Gain
| Budget Range | Best Match |
|---|---|
| Low (under $5K setup) | Barcode or QR |
| Mid ($5K–$25K) | Barcode + Selective RFID Zones |
| High ($25K+) | RFID at scale + Barcode for exceptions |
Your Team Matters More Than Your Tech
-
RFID means retraining + process change
-
Barcode = minimal training, but higher labor
-
QR = fast onboarding, great for temp staff / seasonal surge
“Tech that doesn’t get adopted becomes invisible — and expensive.”
Still unsure? Here’s a tip:
- Test RFID in one receiving dock.
- Keep barcode for pick/pack.
- Use QR for fast-returns.
- Then scale what works.
Pre-Made Warehouse Scenarios (Decision Triggers)
| Warehouse Type | Best System |
|---|---|
| Multi-channel retailer with mobile teams | QR + Barcode |
| 3PL with 4 zones + 10K SKUs | Barcode core + RFID receiving |
| High-volume FMCG brand with automated lanes | RFID with barcode fallback |
| Small warehouse with 3 staff, 1 location | Barcode only |