RFID Tag Types Compared: Passive vs Active vs UHF vs NFC (2025 Expert Guide)
Posted on مايو 31, 2024Choosing the right RFID tag isn’t just about tech — it’s about money, speed, and accuracy.
Get it wrong, and you risk stockouts, scanning errors, and wasted spending. Get it right, and your inventory practically runs itself.
RFID Tag Types Explained
RFID tags come in all types: passive, active, semi-passive, UHF, and NFC — and yes, they all work differently. In this guide, we’ll cut through the jargon and compare every tag type based on what actually matters: cost, range, battery, and real-world performance.In industries like retail, the adoption of RFID is already transforming operations — from faster checkouts to smarter shelf replenishment — as explored in how RFID technology is transforming retail operations.
If you’re wondering:
– “What’s the difference between passive and active RFID?”
– “How far can RFID tags be read?”
– “Which RFID is best for inventory?”
You’re in the right place.
Active vs Passive vs Semi-Passive RFID Tags
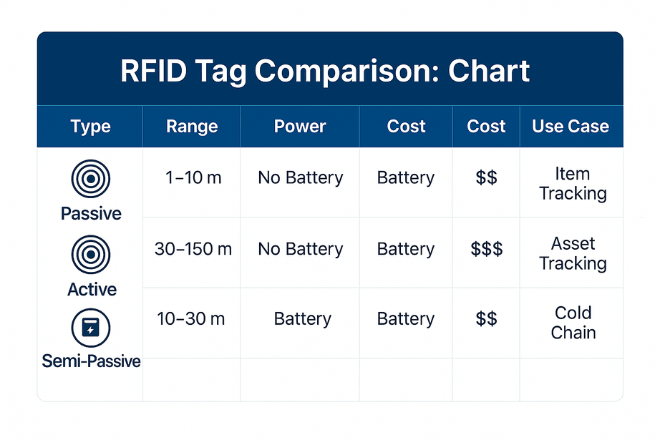
Passive RFID Tags

Passive RFID tags do not contain an internal power source. Instead, they harvest energy from the electromagnetic field emitted by the RFID reader. When the reader transmits a signal, the tag’s antenna captures it, powers the chip momentarily, and transmits the stored data.
-
Typical Range: 1 to 10 meters
-
Power Source: Reader-powered (no battery)
-
Cost: Low (ideal for large-scale item-level tagging)
-
Use Cases: Retail inventory, product labeling, library systems, pallet tracking
- Lifespan: Most passive RFID tags last between 8 to 10 years under normal operating conditions. Since they contain no internal power source, their durability depends largely on the physical tag material and environmental exposure.
Due to their low cost and minimal maintenance, passive tags are widely used for high-volume, low-complexity tracking tasks where long-range and environmental durability are not primary concerns.For deeper insights into how RFID enhances tracking at every level of your warehouse or facility, see our guide on RFID for warehouse tracking.
Active RFID Tags

Active RFID tags are equipped with an onboard battery that powers both the tag’s microchip and its transmitter. This enables them to autonomously emit signals at regular intervals, making them ideal for real-time location tracking without the need for direct reader engagement.
-
Typical Range: 30 to 150 meters
-
Power Source: Internal battery
-
Cost: High
-
Use Cases: Asset tracking in construction, vehicle monitoring, medical equipment tracking, fleet logistics
Active tags are highly effective for applications requiring continuous monitoring or long-range communication, particularly in outdoor or industrial environments.
Semi-Passive RFID Tags (Battery-Assisted Passive)

Semi-passive RFID tags bridge the gap between passive and active technologies. These tags contain a battery that powers the internal circuitry but do not continuously transmit signals. Instead, they activate only when queried by a reader, resulting in better signal strength and improved performance in interference-prone environments.
-
Typical Range: 10 to 30 meters
-
Power Source: Battery-assisted (triggered by reader signal)
-
Cost: Moderate
-
Use Cases: Cold chain monitoring, environmental sensors, high-accuracy location tracking in warehouses
Semi-passive tags are particularly useful in industries that require detailed condition tracking (e.g., temperature, humidity) or where passive tags are insufficient due to environmental constraints.
RFID Frequencies: LF, HF, UHF, and NFC Explained
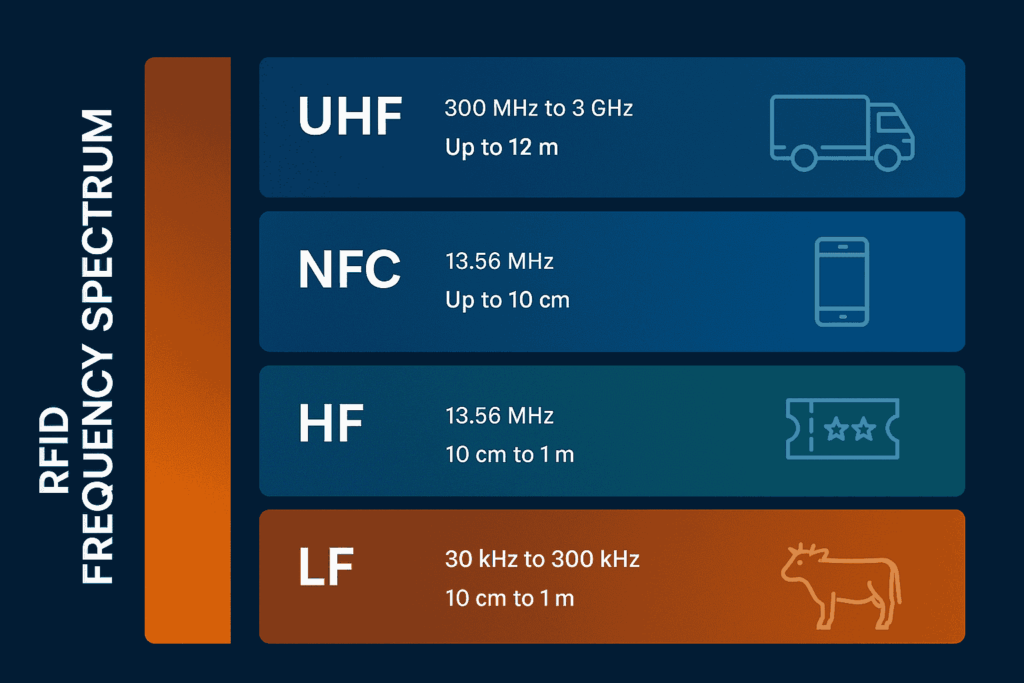
RFID systems operate across multiple frequency bands. The selection of frequency determines key parameters such as read range, speed, signal stability, and material compatibility.
Low Frequency (LF) RFID – 30 KHz to 300 KHz
-
Read Range: Up to 10 cm
-
Strengths: High resistance to water and metal interference
-
Limitations: Slower data transfer rates, limited range
-
Use Cases: Animal tracking, industrial machinery, automotive applications
LF tags are typically used in harsh environments where interference from liquids or metals would compromise higher-frequency tags.
High Frequency (HF) RFID – 3 MHz to 30 MHz
-
Read Range: Up to 1 meter
-
Strengths: Stable read range, larger memory capacity
-
Limitations: Limited range compared to UHF
-
Use Cases: Smart cards, ticketing systems, secure access control, library asset tracking
HF tags balance performance and cost, making them suitable for environments where short-range communication and higher data security are important.
Near Field Communication (NFC) – Subset of HF at 13.56 MHz
NFC tags are a specialized subset of HF RFID that support two-way communication and are designed for proximity-based applications.
-
Read Range: Up to 10 cm
-
Strengths: Two-way interaction, compatible with most smartphones
-
Limitations: One-to-one tag reading, limited scalability for industrial applications
-
Use Cases: Contactless payments (e.g., ApplePay), interactive marketing, consumer electronics
NFC tags are not typically used for inventory tracking, but they offer unique advantages for brand engagement and customer-facing experiences.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF) RFID – 300 MHz to 3 GHz
-
Read Range: Up to 12 meters (extendable under optimal conditions)
-
Strengths: High read speed, long range, bulk reading capability
-
Limitations: Susceptible to interference from liquids and metals
-
Use Cases: Retail inventory, warehouse management, logistics, supply chain automation
UHF RFID is the most widely adopted frequency for enterprise inventory and logistics operations due to its ability to handle large volumes of items in fast-moving environments.
How to Choose the Right RFID Tag for Your Business
Choosing the appropriate RFID tag type is not a matter of preference — it’s a calculated decision that depends on multiple operational and environmental variables. The wrong selection can result in failed reads, system errors, and unnecessary replacement costs. The right choice ensures reliable performance, cost-efficiency, and scalability across your entire inventory or asset tracking system.Choosing the right tag isn’t just about range or frequency — it’s about supporting the right inventory workflow, like cycle counting with RFID instead of relying on outdated physical counts.
Here are the key criteria every business should evaluate when selecting RFID tags:
1. Environment and Material Sensitivity
Question: Will the tags be placed on or near metal surfaces, liquids, or in areas with high electromagnetic interference?
-
Recommended: Use LF or specialized UHF on-metal tags for metal-heavy environments. Semi-passive tags perform better in interference-prone zones due to their stronger return signals.
-
Examples: Auto parts stores, industrial machinery warehouses, breweries
Note: UHF tags generally struggle near liquids and metals unless purpose-built to handle those conditions.
2. Required Read Range
Question: How far away will the reader be from the tag during scanning?
-
Short Range (0–1m): Use HF or NFC tags for secure proximity use cases
-
Medium Range (1–5m): Use passive UHF tags
-
Long Range (10m+): Use active RFID or semi-passive tags
Use Cases:
-
Retail & Inventory: Passive UHF tags for shelf and box-level scanning
-
Yard or Vehicle Tracking: Active RFID for long-distance autonomous updates
3. Mobility and Scanning Speed
Question: Will tags be scanned while in motion (e.g., conveyor belts, vehicles) or stationary?
-
Mobile/High-Speed Use: Choose UHF tags for their fast read rate and multi-tag detection
-
Static Use: HF or passive UHF can be sufficient if items are read individually
This is critical for real-time inventory systems where scanning delays or misreads can bottleneck operations.
4. Data Storage Needs
Question: Do you need to store detailed item-level data on the tag itself?
-
Minimal Data (SKU, ID): Use passive UHF or LF/HF tags
-
High-Volume or Secure Data: Use HF or NFC tags for their larger memory capacity and encryption capabilities
Examples: Product authentication, pharmaceutical labeling, customer-facing smart tags
5. Temperature and Durability Requirements
Question: Will the tag be exposed to extreme heat, cold, moisture, or physical stress?
-
High Durability Required: Use industrial-grade passive or semi-passive tags with rugged casings
-
Cold Chain Applications: Semi-passive RFID tags are often selected for refrigerated environments, as they can power onboard sensors to monitor temperature over time
Selecting tags rated for environmental resilience ensures reliability and longevity, especially in food production, manufacturing, and healthcare settings.
6. Tag Size Constraints
Question: Are the items being tagged small, curved, or space-limited?
-
Small/Curved Surfaces: Use miniature UHF or HF tags with adhesive backing or embeddable design
-
Large Flat Surfaces: UHF inlays or hard tags offer better performance
Jewelry, eyewear, and electronics often require small footprint tags that do not interfere with aesthetics or function.
7. Budget and Volume Considerations
Question: What is the cost sensitivity of your deployment, and how many tags are required?
-
Low-Cost, High-Volume Deployments: Use passive UHF or LF tags
-
High-Performance, High-Value Assets: Consider active or semi-passive tags where ROI justifies the cost
The goal is not to choose the cheapest tag, but the tag that delivers the best long-term return on operational efficiency and accuracy.
8. Integration With Existing Systems
Question: Will the tags integrate with ERP, WMS, or legacy infrastructure?
-
Ensure tag format and memory layout are compatible with your middleware or backend
-
Standard formats such as EPC Gen2 (UHF) are widely supported across modern RFID platforms
Tags must align not just with hardware but also with the software ecosystem — from encoding stations to data pipelines.
RFID Tag Comparison Table
Selecting the right RFID tag is not a one-size-fits-all decision. Every use case comes with unique constraints, and it’s essential to align the physical tag characteristics with the business process it supports.
At Altavant Consulting, we guide businesses through this evaluation with a technical-first lens, helping clients avoid expensive trial-and-error cycles by getting it right from day one. Our approach ensures every RFID deployment delivers measurable impact — whether in operational visibility, audit compliance, or inventory accuracy.
Whether you’re scanning product-level SKUs or tracking pallets in a multi-site network, understanding RFID’s benefits for inventory management is critical to choosing the right tag type.
| Tag Type | Power Source | Read Range | Durability | Data Capacity | Cost per Unit | Primary Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passive RFID (UHF) | No battery (reader-powered) | 1 – 10 meters | Moderate (varies by casing) | Low (ID, SKU, basic data) | Low | Retail inventory, warehouse pallets, product labeling |
| Active RFID | Internal battery | 30 – 150 meters | High (robust housing, outdoor-rated) | Medium–High (frequent updates) | High | Construction equipment, hospital assets, vehicle fleets |
| Semi-Passive RFID | Battery-assisted (reader-activated) | 10 – 30 meters | Moderate–High (industrial-grade) | Medium–High (sensor data) | Moderate | Cold chain, environmental monitoring, warehouse item tracking |
| HF RFID (13.56 MHz) | No battery | 10 cm – 1 meter | Moderate | Medium (multi-sector memory) | Low–Moderate | Access control, library systems, transit, pharma compliance |
| NFC (Subset of HF) | No battery | Up to 10 cm | Moderate | High (two-way capability) | Moderate | Smart labels, marketing engagement, contactless payments |
| LF RFID (125 KHz) | No battery | Up to 10 cm | Very High (resistant to metal/water) | Low | Low–Moderate | Industrial machinery, animal tagging, secure access |
Additional Notes:
-
Battery life for active/semi-passive tags typically ranges from 2 to 5 years, depending on transmission interval and environment.
-
Durability ratings should always be reviewed at the product level — tag encapsulation, adhesive strength, and material resistance vary widely.
-
Cost ranges are relative and depend heavily on tag volume, supplier agreements, and custom encoding requirements.
Talk to an RFID Expert
Not sure which RFID tag is best for your environment or workflow?
At Altavant Consulting, we’ve helped leading retailers, manufacturers, and logistics teams implement RFID solutions tailored to their exact business needs — from hardware selection to system integration.
If you’re evaluating RFID tags for inventory, cold storage, or asset tracking, our specialists can help you avoid costly missteps and build a system that scales.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between passive and active RFID tags?
Passive RFID tags do not contain a power source and rely on the reader’s signal to activate and communicate. Active RFID tags have a built-in battery that allows them to broadcast signals independently, enabling longer read ranges and real-time tracking. Passive tags are more affordable and used for item-level inventory, while active tags are preferred for high-value asset tracking across larger distances.
What is a semi-passive RFID tag?
A semi-passive RFID tag includes an internal battery that powers the chip but does not actively transmit unless triggered by a reader. This results in stronger reflected signals, greater read reliability in difficult environments, and longer read ranges than traditional passive tags.
What is the maximum range for RFID tags?
Passive UHF tags typically offer a range of 1 to 5 meters. Semi-passive tags extend that to 10–30 meters, while active RFID tags can reach up to 150 meters under ideal conditions. Actual range depends on tag type, reader power, and environmental interference.
How do I choose the right RFID tag?
Choosing the right RFID tag depends on your required read range, material compatibility, environmental conditions, data storage needs, and integration requirements. Passive tags are best for basic item-level tracking. Active and semi-passive tags are suited for long-range, real-time, or harsh environments.
Can passive RFID tags be tracked in real time?
No. Passive RFID tags cannot be tracked in real time because they lack internal power. They only transmit when activated by a reader signal. For real-time visibility, active RFID tags are required.
What’s the difference between HF, UHF, and NFC tags?
HF tags operate around 13.56 MHz and are used in secure access and transit. UHF tags operate up to 3 GHz and are optimized for long-range, high-speed scanning in inventory systems. NFC tags are a subset of HF, allowing two-way data exchange with smartphones at close range.
Do RFID tags need batteries?
Only active and semi-passive RFID tags have internal batteries. Passive RFID tags do not require a battery and are powered solely by the RFID reader’s signal.
Can I read RFID tags with a smartphone?
Only NFC tags can be read by most smartphones. Other RFID formats, including UHF, require specialized RFID reader hardware.
Are there industry standards for RFID tags?
Yes. EPC Gen2 is the standard for UHF RFID in logistics and retail. ISO 14443 and ISO 15693 are standards for HF/NFC tags used in identity cards and smart ticketing systems.
What is the most commonly used RFID tag?
The most widely used RFID tag is the passive UHF tag, especially those adhering to EPC Gen2 standards. These are prevalent in retail, warehousing, and supply chain environments.